Introduction to Mount Rinjani and Its Significance in Indonesia
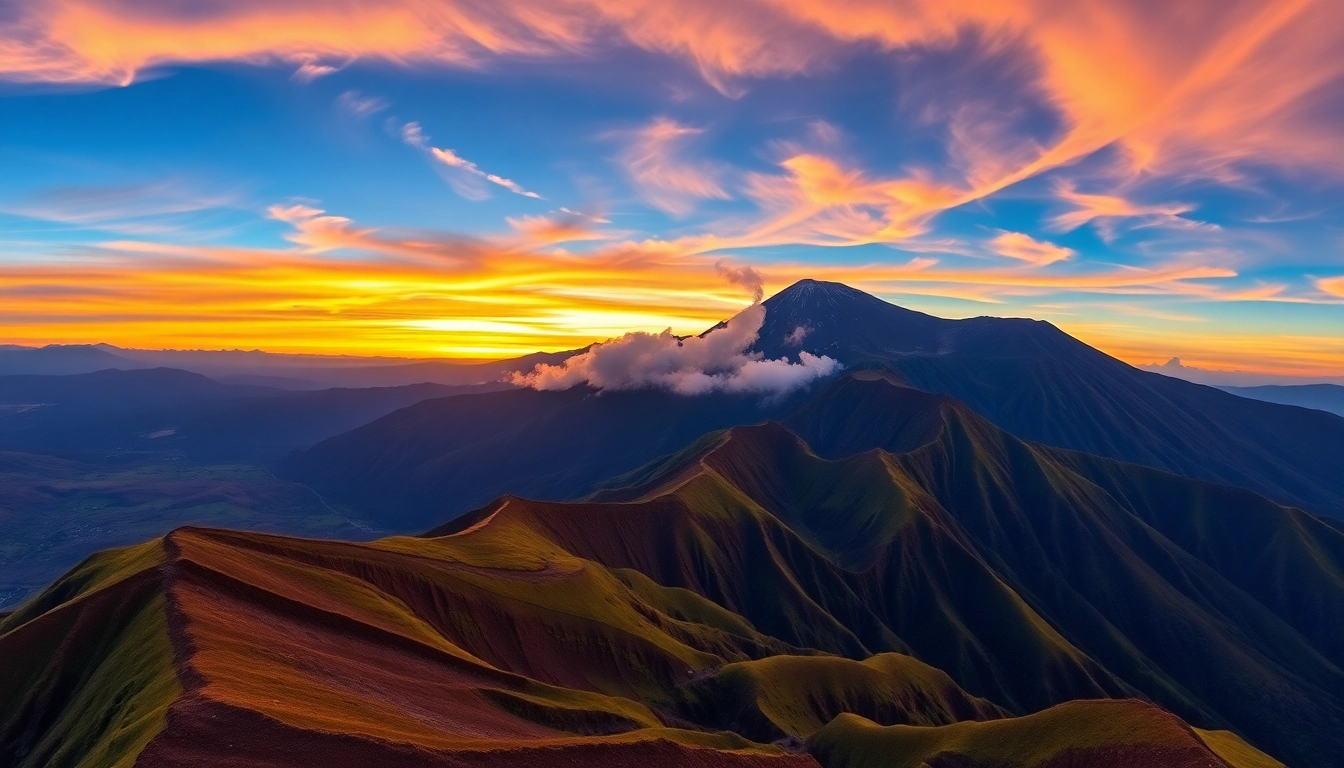
Mount Rinjani stands as Indonesia’s second-highest volcano and one of the most iconic natural landmarks in Southeast Asia. Located on the island of Lombok, this active stratovolcano not only draws adventure seekers and nature enthusiasts but also holds profound cultural, geological, and ecological significance. Its towering presence, reaching 3,726 meters above sea level, offers breathtaking panoramic views and diverse ecosystems that range from lush rainforests to barren volcanic landscapes.
If you’re intrigued by volcanic scenery or seeking an unforgettable adventure, exploring Mount Rinjani provides an immersive experience into Indonesia’s majestic natural heritage. Its prominence in local culture, combined with its stunning geological features, makes it a must-visit destination for travelers and researchers alike.
Geographical Location and Volcanic Features
Geographically, Mount Rinjani is situated in North Lombok Regency, within the boundaries of the Rinjani National Park. The park spans over 41,330 hectares, encompassing diverse habitats and geological formations. The volcano features a spectacular caldera, approximately 8 by 10 kilometers in size, which shelters the stunning Segara Anak Lake—a major highlight of the region.
The volcano itself is a complex stratovolcano, characterized by its impressive summit crater, hot springs, fumaroles, and other geothermal activity indicative of its active status. The cone vent, with other secondary craters, emits smoke and occasional ash plumes, reminding visitors of its eruptive potential. Beneath the surface, the volcano’s internal activity is monitored continuously to understand the geodynamics and mitigate potential hazards.
Historical Eruptions and Geological Formation
Mount Rinjani’s geological history dates back thousands of years, with its most significant eruption believed to occur around the late 13th century, notably the eruption of the Samalas volcano in 1257. This eruption is considered one of the largest in Indonesia’s recorded history, impacting global climate through the massive release of volcanic ash and aerosols, which led to a period of volcanic winter effects worldwide.
The formation of Rinjani and its caldera reflects a dynamic volcanic process involving multiple phases of eruptions, collapses, and lava flows. Its geological evolution has shaped Lombok’s landscape, carving valleys, creating fertile volcanic soils, and forming features like hot springs and waterfalls.
Cultural and Ecological Importance in Lombok
Beyond its geological significance, Mount Rinjani holds deep cultural importance for the Sasak and Lombok communities. The mountain is often regarded as sacred, and local legends attribute spiritual power to its summit and surrounding areas. Numerous temples and ritual sites are found on and around the volcano, where traditional ceremonies are performed to honor the mountain and seek blessings.
Ecologically, Rinjani National Park is a biodiversity hotspot, home to a wide range of flora and fauna endemic to Wallacea’s transitional zone. The park’s ecosystems include montane forests, grasslands, and alpine zones, providing habitats for endangered species like the Rinjani scops owl, Lombok kingfisher, and several Tikus rodents. The park’s conservation efforts aim to preserve its unique biodiversity while promoting sustainable tourism that benefits local communities.
Planning Your Trekking Adventure on Mount Rinjani
Best Seasons and Optimal Times for Trekking
Ideal trekking seasons on Mount Rinjani occur during the dry season, typically from May to September, when weather conditions favor safe and comfortable hikes. During this period, the skies are clearer, temperatures are moderate, and trail conditions are less muddy and treacherous. The peak months of July to August are particularly popular, attracting a large number of trekkers from around the world.
It is advisable to avoid the rainy season (November to March), as heavy rainfall can increase the risk of landslides, trail erosion, and poor visibility. Moreover, slightly cooler climate at higher altitudes requires proper preparation regardless of the season.
Required Gear and Safety Precautions
Preparing adequately for the Rinjani trek is crucial for safety and enjoyment. Essential gear includes durable hiking boots, layered waterproof clothing, warm insulating layers (especially for nights at higher elevations), a hat, gloves, trekking poles, and a reliable headlamp. Given the high altitude, altitude sickness can be a concern; acclimatization days and hydration are vital.
Safety precautions extend beyond gear. Always trek with certified guides and reputable tour operators who are knowledgeable about current trail conditions and emergency protocols. Carry a basic first aid kit, personal medications, and a communication device for emergencies, especially since mobile coverage may be limited in remote areas.
Choosing Certified Guides and Tour Operators
To ensure a safe and respectful trekking experience, select guides and operators who are certified by local authorities and have positive reputations. GPS-tracked tours, small group sizes, and transparent pricing are markers of quality service. Guides should be trained in first aid, environmental conservation, and cultural sensitivity.
Researching reviews, seeking recommendations from experienced trekkers, and verifying permits and insurance coverage are recommended steps before booking your adventure. Supporting responsible tourism also involves respecting local customs and minimizing environmental impact.
Step-by-Step Mount Rinjani Trekking Routes
Sembalun and Senaru Trail Options Overview
There are two main routes to ascending Mount Rinjani: the Sembalun route and the Senaru route, each offering unique experiences. The Sembalun trail, starting from the east, is known for its gradual ascent across open grassy plains, offering expansive views of the volcano and surrounding landscapes. The Senaru trail, from the north, is characterized by lush rainforests and steeper terrain, providing a more challenging but richly scenic route.
Both routes converge at the crater rim, where trekkers can enjoy stunning vistas of the Segara Anak Lake and the active summit crater.
Difficulty Levels and Duration Estimates
The Sembalun route is generally considered moderate, taking about 2-3 days to reach the crater rim, with an additional day for descent. The Senaru route is more challenging, often requiring 3-4 days to complete, depending on acclimatization and pace. Altitude sickness, steep descents, and variable weather conditions contribute to the difficulty levels.
Proper physical preparation, acclimatization plans, and flexible scheduling help mitigate risks and ensure successful summiting.
Highlights and Key Landmarks Along the Trail
- Morning and Evening Views: Spectacular sunrises and sunsets illuminate the volcanic landscape, offering some of the most iconic photo opportunities.
- Hot Springs: Located near the crater, these natural thermal baths provide relaxation after a challenging hike.
- Segara Anak Lake: A stunning crater lake with turquoise waters, accessible on the trek and a central point for camping.
- Crater Rim Campgrounds: Campsites that offer panoramic views of the surrounding caldera and beyond.
- Active Summit Crater: The top of Mount Rinjani features fumaroles and the volcano’s fiery crater, a truly awe-inspiring sight.
Top Attractions and Natural Wonders of Mount Rinjani
Lake Segara Anak and Caldera Views
The caldera formed by ancient eruptions hosts Lake Segara Anak, Indonesia’s second-largest volcanic crater lake. Its vivid turquoise hues contrast sharply with the dark volcanic rocks, creating a surreal landscape. Visitors can trek down to the lake, enjoy boat rides, or camp along its shores, soaking in the tranquility and breathtaking scenery.
Rinjani Waterfalls and Hot Springs
The park is dotted with waterfalls such as Tiu Kelep and Sendang Gile in the Senaru region, accessible via guided forest treks. These cascades add to the allure of the park’s ecosystem. The hot springs near the crater and along the trails serve as natural geothermal spas, offering soothing warmth amid the rugged terrain.
Unique Flora and Fauna within Rinjani National Park
Rinjani’s ecological zones host a variety of endemic and migratory species. The montane forests are home to unique orchids, rhododendrons, and medicinal plants, supporting local traditional medicine. Birdwatchers can spot rare species like the Rinjani scops owl, green peafowl, and hornbills. Conservation efforts focus on protecting these fragile habitats while promoting eco-tourism.
Post-Trek Tips and Responsible Tourism
Environmental Conservation Practices
Trekkers are urged to practice Leave No Trace principles—carry out all trash, avoid disturbing wildlife, and stay on marked paths. Local authorities and park management have implemented regulations like designated camping zones and permit systems to manage tourism impact.
Supporting local conservation initiatives, such as reforestation projects and community-based tourism, helps sustain the natural environment for future generations.
Cultural Respect and Community Support
Engaging respectfully with indigenous communities and participating in village-based tourism programs benefits local residents economically and socially. Learning about their customs, dress, and spiritual beliefs creates meaningful interactions. Always seek permission before photographing cultural sites and adhere to local etiquette.
Maximizing Your Experience and Safety During Ascent
Preparation is key to a successful trek. Acclimate gradually, stay hydrated, and avoid pushing beyond your limits. Be attentive to weather changes, which can be sudden and severe at high elevations. Hiring experienced guides ensures proper navigation, safety protocols, and cultural insights, enriching your journey with local knowledge.